More Plastic Bag Manufacturers
Applications
Plastic bags serve as versatile vessels for packaging, shipping, and transporting a wide range of goods across residential, industrial, and commercial sectors. They excel in safeguarding contents from various environmental threats, notably moisture.
Industries ranging from chemical, electronic, construction, automotive, sanitation and waste management, storage, shipping, retail, to pharmaceuticals extensively leverage the advantages offered by plastic bags. Beyond these sectors, plastic bags are also commonly used in households and office environments.
The History of Plastic Bags
Since the 1950s, plastic bags have become ubiquitous. Before then, paper was the primary material for packaging. However, during World War II, American and European manufacturers hurriedly developed plastic formulations for wartime needs. Post-war economic expansion spurred these manufacturers to introduce plastic packaging, such as bags, to consumers. Early versions typically lacked handles, as adding them was costly and required a separate manufacturing process that many producers initially bypassed.
In the 1950s and 1960s, significant milestones marked the evolution of plastic bags. For instance, in 1957, manufacturers introduced the first sandwich baggies on a roll. The following year, dry cleaners transitioned from using traditional brown paper bags to plastic dry cleaning bags. Meanwhile, during the early 1960s, Swedish engineer Sten Gustaf Thulin revolutionized the shopping experience with his innovative design of the modern plastic shopping bag. These bags were noted for their lightweight, flexibility, and durability, and Thulin ingeniously streamlined the process of adding handles, making them more efficient and less time-consuming. Patented by Celloplast in 1965, the one-piece shopping bags quickly gained popularity. By 1977, the US government invalidated the patent, opening up the market for widespread competition among companies.
In 1966, plastic bags became increasingly popular, with 25% to 30% of bread already packaged in this new material. Around the same time, major grocery chains like Kroger started using plastic bags on rolls in their stores. By 1969, the New York City Sanitation Department conducted trials, substituting curbside metal trash can pickups with plastic bags. They discovered that collecting trash and refuse stored in plastic bags was quieter, safer, and more sanitary, contributing significantly to the rise of plastic drum liners.
In 1973, manufacturers cracked the code on producing plastic grocery bags efficiently and affordably for widespread use. Soon after, stores swiftly transitioned from paper bags to plastic or offered them as a convenient choice. By the mid-1970s, major retailers such as J.C. Penney and Sears adopted sealable plastic bags for storing and shipping their products.
Since 1990, cities initiated the pioneering blue bag curbside recycling programs, marking the dawn of consumer recycling. By 1992, nearly half of America’s grocery stores facilitated plastic bag recycling services. Certain regions and states even implemented bans on select plastic bag products in a bid to safeguard the environment from unchecked plastic waste.
Today, the world of plastic bags offers unprecedented versatility and variety. Manufacturers effortlessly craft custom bags in an array of shapes and sizes. Yet, the pivotal challenge facing both producers and consumers lies in enhancing environmental stewardship through increased reuse and recycling efforts. Despite plastic grocery bags dominating the U.S. market at 80%, the recycling rate for consumer plastics barely exceeds 0.5%.
Design
Production Process
The film covering the bag is crafted through blown film extrusion, sheet extrusion, winding, or casting. Blown film extrusion, also referred to as tubular film extrusion, stands as the predominant method for manufacturing plastic bags.
During blown film extrusion, manufacturers kickstart the process by melting polymer resin into a thick, molten liquid. This molten material is then pushed through an annular slit die to shape a thin-walled plastic tube. As the tube emerges, cool air is jetted through the die’s center, inflating the tube into a bubble. Simultaneously, a high-speed air ring blows cool air onto this expanding film bubble. Once sufficiently cooled, the film is guided through flattening rolls. Post-flattening, manufacturers can slit the film to form multiple sheets. These sheets can then be wound onto reels or laid flat for further processing, such as treating bag seams through methods like gluing, heat-sealing, or stitching. Beyond initial fabrication, additional processes like screen printing can enhance the bags’ appearance and functionality.
Materials
Plastic bags are crafted from significant quantities of materials to meet the expanding array of applications they serve. Typically composed of various polymers—organic, natural, or synthetic—the primary choices for manufacturers are polyethylene (including high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and biodegradable LDPE) and polypropylene. These thermoplastics are prized for their lightweight nature and robust durability. Biodegradable options like LDPE have gained popularity, facilitating the rise of reusable plastic bags across multiple industries. They also provide a viable alternative in regions where non-recyclable or non-degradable bags have been restricted.
Vinyl, derived from polyvinyl chloride, stands out as another widely embraced plastic variant. Its durability surpasses that of other plastics, making vinyl bags ideal for robust uses like storage in demanding environments.
Considerations
When customizing plastic bags, manufacturers carefully evaluate several application variables: the intended environmental conditions, the necessary level of content protection, weight specifications, and the potential for reusability. These considerations guide decisions on material composition, treatment methods, dimensions, style options, closure mechanisms, and production costs. Moreover, recyclability remains a critical factor in the design process.
The size of a bag should suit its intended use, as it can range from just a few cubic inches to several hundred. Manufacturers determine the bag’s capacity by multiplying its length, height, and width. Beyond volume, they meticulously assess dimensions, particularly for items of irregular shape.
Depending on how you plan to use the bag, its style, closure, shape, color, and size can vary. Manufacturers offer customization options such as bespoke printed designs, personalized labels or logos, drawstrings, and stretch film to tailor the bags to your needs.
Types
Medical bags serve as essential tools for healthcare providers and, at times, patients, facilitating the storage, transportation, and disposal of medical specimens, supplies, or waste. Typically transparent, they are crafted from durable materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or vinyl, engineered to withstand environmental factors like heat and UV light. This durability ensures prolonged sterility, crucial for maintaining medical safety standards.
The latter variety of plastic bags finds use in critical applications requiring sterilization, such as packaging medical supplies, food items, biological materials, and chemicals.
Shopping bags, commonly referred to as retail bags, serve as carriers for consumers to transport merchandise within stores and to their vehicles. Similar to medical bags, they are typically crafted from materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene, or vinyl.
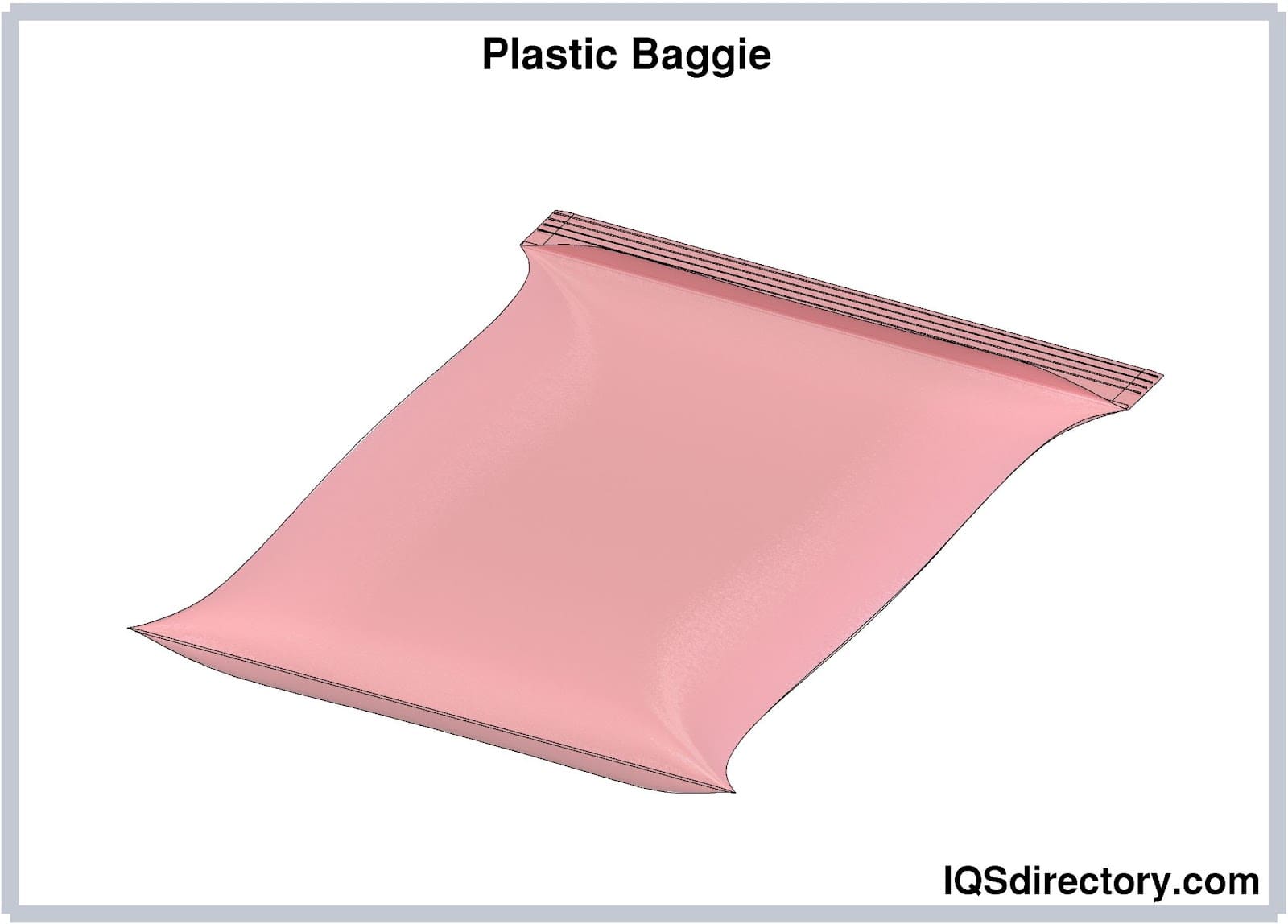
Resealable bags, often referred to as re-closable bags, offer the convenience of multiple openings and closures. They utilize mechanisms such as plastic zippers or interlocking profiles to create a secure seal. Among the well-known variants is the Ziploc bag, famous for its reliability. These bags play a crucial role in reducing plastic consumption and waste by promoting reuse. Widely embraced in both household settings and the food service industry, they exemplify practical sustainability practices.
Ziploc bags, beloved for their resealable design, first hit the market in 1968 under the Dow Chemical Company’s banner. Today, they continue to thrive under the ownership of S.C. Johnson & Son.
Clear plastic bags are frequently chosen for merchandise because they offer consumers the ability to preview the contents before making a purchase.
Wicket bags revolutionize high-speed industrial product storage by slashing handling times. Hung on a “U” shaped metal ring, they remain closed except for a single opening. When needed, an automated system effortlessly inflates them, ready to swiftly receive products. These bags boast USDA approval, ensuring their reliability for food storage.
Retailers employ food packaging bags to encase store-bought food items. These bags are meticulously designed to ensure sterility and withstand potential damage and chemical leaching caused by factors such as heat and UV light.
Drum liners are durable plastic bags designed to neatly contain and secure the contents of garbage cans. Their robust construction ensures they remain intact even when users are removing them filled with trash.
Gusset bags are specialized plastic pouches crafted to accommodate sizable, unwieldy items or tiny, free-flowing goods like soil, candy, or hardware. Their distinctive sides and bottoms ensure they excel at their task.
Advantages of Plastic Bags
Plastic bags boast a range of advantages. Firstly, their production costs are significantly lower compared to containers crafted from materials like metal. Secondly, they exhibit remarkable versatility, adaptable for virtually any purpose through innovative design by manufacturers. Moreover, across multiple industries, users rely heavily on them in daily operations because plastic bags, unlike their paper counterparts, offer flexibility, sturdiness, durability, and excellent tear resistance. Another notable benefit is their high recyclability, making them a sustainable choice for many.
Standards
The requirements for your plastic bags vary based on your industry, application, and location. For instance, gusset bags intended for food storage require USDA approval, while those used in medical contexts must meet FDA standards.
Certain states, like California, enforce restrictions on bag thickness to discourage the production and use of single-use bags. California has additionally prohibited retailers from providing plastic shopping bags, part of its strategy to combat plastic waste. Other states have adopted similar bans. Therefore, it’s crucial to investigate the regulations and potential bans in your state. All plastic bags manufactured and used in the United States must comply with the US Code of Federal Regulations (CFR).
Things to Consider
If you’re seeking top-notch plastic bags tailored to your needs, we recommend partnering with a reputable manufacturer specializing in high-quality plastics. To guide your search, we’ve curated a selection of our top recommendations. Each of these manufacturers is seasoned and verified. Explore their websites to discover the diverse range of services and products they offer. Links to their detailed profiles can be found above. Rest assured, the ideal manufacturer for you is among them. Choose one that not only offers competitive deals but also aligns perfectly with your specific requirements and budget.
Check out our Plastic Tubing website











 Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard Tubes Carrying Cases
Carrying Cases Contract Packaging
Contract Packaging Corrugated Boxes
Corrugated Boxes Dot Peening Machines
Dot Peening Machines Labeling Machinery
Labeling Machinery Marking Machinery
Marking Machinery Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Palletizers
Palletizers Plastic Bags
Plastic Bags Sewing Contractors
Sewing Contractors Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services